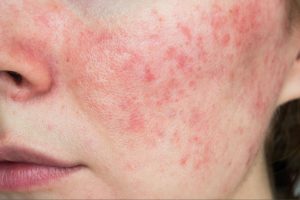
 Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE), commonly known as lupus, is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects multiple organs and systems in the body. Although there is no cure for lupus, there are various treatment options available to manage symptoms, prevent flares, and minimize organ damage. In this article, we will explore the different treatment approaches for lupus and discuss their benefits and considerations.
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE), commonly known as lupus, is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects multiple organs and systems in the body. Although there is no cure for lupus, there are various treatment options available to manage symptoms, prevent flares, and minimize organ damage. In this article, we will explore the different treatment approaches for lupus and discuss their benefits and considerations.
Medications for Lupus Treatment
Medications play a crucial role in managing lupus symptoms and controlling the underlying inflammation. The specific drugs prescribed depend on the individual’s symptoms, the severity of the disease, and the organs affected. Here are some commonly used medications for lupus treatment:
1. Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, or NSAIDs, are often the first line of treatment for mild to moderate lupus symptoms. These medications help reduce pain, swelling, and fever associated with the disease. Over-the-counter NSAIDs like naproxen sodium and ibuprofen are readily available, while stronger NSAIDs may require a prescription. It’s important to note that long-term use of NSAIDs can have side effects, such as stomach bleeding, kidney problems, and an increased risk of heart problems.
2. Antimalarials
Antimalarial drugs, such as hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil), are commonly used to treat lupus. These medications not only help control symptoms like fatigue, joint pain, and skin rashes but also reduce the risk of flares. Antimalarials are considered relatively safe, with potential side effects including stomach upset and, rarely, damage to the retina. Regular eye exams are recommended for individuals taking these medications.
3. Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids, such as prednisone, are potent anti-inflammatory drugs that help suppress the immune response in lupus. They are often used for short-term management of severe symptoms or during lupus flares. However, long-term use of corticosteroids can lead to various side effects, including weight gain, easy bruising, thinning bones, high blood pressure, diabetes, and an increased risk of infection. Doctors aim to prescribe the lowest effective dose and duration to minimize these risks.
4. Immunosuppressants
In more serious cases of lupus, when organ involvement is significant, immunosuppressant medications may be prescribed. These drugs work by suppressing the overactive immune system responsible for the inflammation in lupus. Examples of immunosuppressants used in treating lupus include azathioprine, mycophenolate, methotrexate, cyclosporine, and leflunomide. While these medications can be effective in managing lupus, they may increase the risk of infections, liver damage, decreased fertility, and certain types of cancer.
5. Biologics
Biologic medications, such as belimumab (Benlysta) and rituximab (Rituxan, Truxima), specifically target components of the immune system involved in lupus. Belimumab, the only FDA-approved biologic for lupus, can reduce lupus symptoms in some individuals. Rituximab may be beneficial for those who have not responded to other treatments. These biologics come with potential side effects, including nausea, diarrhea, infections, and, in rare cases, worsening of depression.
Additional Therapies for Lupus Management
In addition to medications, some individuals may explore alternative and complementary therapies to help manage their lupus symptoms. While research on these therapies is limited, some people report finding relief with the following approaches:
1. Special Diets and Nutritional Supplements
Certain diets, such as the anti-inflammatory diet or the Mediterranean diet, may help reduce inflammation and improve overall health. Some individuals also turn to nutritional supplements like fish oils, vitamin D, or specific antioxidants to support their immune system and manage symptoms. It’s important to discuss dietary changes and supplements with a healthcare professional to ensure they are safe and appropriate.
2. Topical Ointments and Creams
Topical ointments and creams can provide relief for skin rashes and joint pain associated with lupus. These products typically contain anti-inflammatory ingredients that help soothe the affected areas. However, it’s essential to consult with a dermatologist or rheumatologist before using any topical treatments to ensure their efficacy and safety.
3. Mind-Body Practices
Mind-body practices, such as acupuncture, chiropractic treatment, and homeopathy, are often sought after by individuals with lupus. While these therapies may offer some relief, their effectiveness in managing lupus symptoms is not well-established. It’s crucial to consult with trained professionals and discuss potential benefits and risks before pursuing these practices.
Treating Lupus-Related Complications
Lupus can cause various complications that require targeted treatment. Depending on the specific complications, additional medications may be prescribed alongside lupus treatment. Here are some common complications and their corresponding treatments:
1. Anticonvulsants for Seizures
Seizures can occur in individuals with lupus, and anticonvulsant medications may be prescribed to manage them. These medications help control and prevent seizures, improving overall quality of life for those affected.
2. Antibiotics for Infections
Lupus can weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections. If an infection occurs, antibiotics may be necessary to treat and resolve the infection promptly.
3. Antihypertensive Drugs for High Blood Pressure
High blood pressure, or hypertension, is a common complication of lupus. Antihypertensive medications are prescribed to help manage and control blood pressure levels, reducing the risk of cardiovascular complications.
4. Statins for High Cholesterol
Elevated cholesterol levels are also prevalent in individuals with lupus. Statin medications may be prescribed to lower cholesterol levels, reducing the risk of heart disease and other cardiovascular problems.
5. Drugs for Osteoporosis
Lupus and its treatments can contribute to the development of osteoporosis, a condition characterized by weakened bones. Medications such as bisphosphonates may be prescribed to prevent or treat osteoporosis and reduce the risk of fractures.
Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle with Lupus
In addition to medical treatments, maintaining a healthy lifestyle is crucial for individuals with lupus. Here are some lifestyle factors that can positively impact lupus management:
Heart-Healthy Diet
Following a heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains can support overall well-being and reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications. It’s essential to consult with a registered dietitian to develop a personalized diet plan that meets your nutritional needs.
Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight can help alleviate stress on the joints and reduce the risk of other health complications, such as cardiovascular disease. Regular exercise and a balanced diet are key components of weight management.
Regular Exercise
Engaging in regular physical activity can help improve strength, flexibility, and overall well-being. Low-impact exercises, such as walking, swimming, or yoga, can be beneficial for individuals with lupus. However, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional or physical therapist before starting an exercise routine to ensure it is safe and appropriate for your condition.
4. Sun Protection
Ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun can trigger lupus flares and worsen skin symptoms. It’s important to minimize sun exposure by wearing protective clothing, using sunscreen with a high SPF, and seeking shade during peak sun hours.
5. Infection Prevention
Due to the weakened immune system associated with lupus and certain medications used in treatment, individuals with lupus are more susceptible to infections. It’s crucial to practice good hygiene, receive recommended vaccinations, and promptly seek medical attention for any signs of infection.
6. Avoid Smoking
Smoking can worsen lupus symptoms and increase the risk of cardiovascular complications. Quitting smoking or avoiding exposure to secondhand smoke is essential for individuals with lupus.
Regular Monitoring and Communication with Healthcare Providers
Regardless of the treatment plan chosen, regular monitoring and open communication with healthcare providers are vital for successful management of lupus. This allows for adjustments in medications, therapies, or lifestyle recommendations as needed. It’s important to attend regular check-ups, follow-up appointments, and laboratory tests to track the progression of the disease and identify any potential side effects or complications.
While there is no cure for lupus, there are multiple treatment options available to manage symptoms, prevent flares, and minimize organ damage. Medications, including NSAIDs, antimalarials, corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, and biologics, are commonly prescribed to control inflammation. Alternative therapies, such as special diets, ointments, and mind-body practices, may offer additional support. Treating lupus-related complications and maintaining a healthy lifestyle are also crucial aspects of managing the disease. Regular monitoring and communication with healthcare providers ensure that the treatment plan remains effective and tailored to individual needs.
Contact Us (859-331-3100) For More Information or to Request an Appointment
—
 About Tristate Arthritis and Rheumatology
About Tristate Arthritis and Rheumatology
Tristate Arthritis and Rheumatology is the first and largest Rheumatology practice in the Northern Kentucky area. Founded by Dr. Arthur Kunath in 1986, our rheumatology practice now consists of six doctors who are board certified in both Internal Medicine and Rheumatology and a Physician Assistant. Patients see one doctor (except in emergencies), thereby assuring continuity of care and an individualized docteor-patient atmosphere giving the physician the ability to establish personalized and detailed relationships. Our doctors have received numerous awards, including being listed as “Top Doctors” in Cincinnati Magazine, receiving the Patient’s Choice Award, the Most Compassionate Doctor Award, and the American College of Rheumatology’s “My Doc Rocks” award.


